A detailed explanation of the differences between Shockwave therapy and 810nm 980nm laser therapy
Shockwave therapy and laser therapy—typically referring to low-intensity laser therapy or photobiomodulation therapy—are two important non-invasive physical therapy techniques in modern rehabilitation medicine. Although both aim to relieve pain and promote tissue repair, they differ fundamentally in their working principles, applicable conditions, and treatment experience.
一、Core Principle: The Fundamental Differences Between Mechanical Force and Light Energy
1. Shockwave therapy
Shockwave therapy uses high-energy, high-intensity sound waves generated by an external device. These waves are produced using electromagnetic, pneumatic, or piezoelectric principles. Delivered in pulses, these sound waves penetrate soft tissues such as skin and fat without attenuation, precisely delivering energy to deep-seated areas of pathology in bones, tendons, and fascia. The core principle is the transmission and conversion of mechanical energy.
2. 810nm and 980nm laser therapy –low-intensity laser therapy
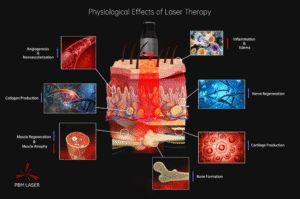
This technology uses low-intensity lasers, emitting coherent light with wavelengths of 810nm -near-infrared band and 980nm -infrared band. Light at these wavelengths has excellent penetration capabilities into human tissue. During treatment, the photon beam is directed onto the body surface, and the light energy penetrates the tissue and is absorbed by the cells. The core principle is the transfer of light energy and its subsequent biochemical transformation.
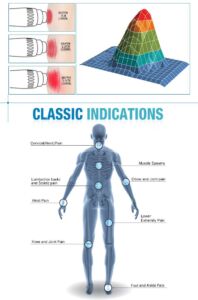
二、Main Indications: Powerful Tools for Different Problems Due to their differing principles, the optimal indications for the two therapies are also distinctly different.
Shockwave therapy is primarily suitable for:
Chronic, refractory soft tissue disorders: especially those that do not respond well to conventional physical therapy .
Plantar fasciitis.
Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis), golfer’s elbow.
Frozen shoulder -especially calcific tendinitis of the rotator cuff.
Achilles tendinitis, patellar tendinitis.
Myofascial pain syndrome: used to release “trigger points” in the muscles.
Nonunion/delayed union of fractures: to promote fracture healing.

Typical indications for 810nm 980nm laser therapy:
Various acute and chronic inflammatory conditions: such as arthritis, bursitis, and tenosynovitis.
Acute soft tissue injuries: muscle strains, ligament sprains, and overuse injuries.
Difficult-to-heal wounds and ulcers: such as diabetic foot ulcers and pressure ulcers.
Neuropathic pain: such as trigeminal neuralgia and postherpetic neuralgia.
Post-operative rehabilitation: used to control pain, reduce swelling, and accelerate wound healing.

三、Treatment Experience and Course: A Comparison of Sensations and Cycles
1 Treatment experience:
Shockwave therapy: The treatment process is usually accompanied by noticeable sensations of soreness, numbness, and swelling, and the pain may be more intense at higher energy levels. After treatment, the treated area may experience temporary redness, swelling, soreness, or slight bruising, which are normal treatment reactions.
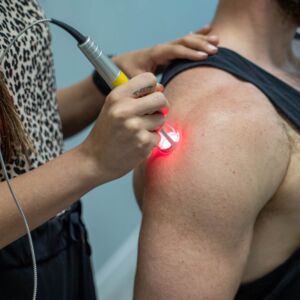
810nm 980nm Laser physiotherapy: The treatment process is basically painless and very comfortable. Patients usually only feel the contact of the treatment probe with the skin, and sometimes a slight warming sensation. It is a completely painless treatment.
2 Treatment duration:
Shockwave therapy: Short treatment course, long intervals between sessions. Typically, one course of treatment requires 3 to 5 sessions, with each session spaced 5 to 7 days apart, or even longer, to allow the body sufficient time to activate its repair mechanisms. The effects are often not immediate but gradually become apparent within a few weeks after treatment.
810nm 980nm Laser physiotherapy: Relatively longer treatment course, higher frequency. Typically requires 5 to 20 sessions, and depending on the severity of the condition, treatment may be needed 2 to 5 times per week. For acute inflammation, the effects may be felt more quickly.
四、Contraindications
1. Shockwave Therapy
Contraindications include:
Individuals with a bleeding tendency (such as coagulation disorders, or those currently taking anticoagulants);
Pregnant women (treatment is prohibited in the abdominal and pelvic areas);
Individuals with implants in the treatment area (such as pacemakers, artificial joints, metal stents);
Individuals with malignant tumors;
Adolescents with unfused epiphyses (avoid treatment in bone growth areas);
Patients in the acute phase of infectious inflammation.
2.810nm 980nm Laser Therapy
Individuals sensitive to light (such as patients with lupus erythematosus, or those currently taking photosensitive medications);
Avoid direct irradiation of the eyes (the eyeballs must be avoided);
Individuals with malignant tumors;
Individuals with uncontrolled infectious lesions;

五、Summary and Treatment Recommendations:
The core advantage of Shockwave therapy lies in its ability to stimulate the body’s deepest repair mechanisms, essentially pressing the “restart” button on the body’s repair process for damaged areas. Shockwave therapy should be considered a priority treatment option when a clinical diagnosis clearly indicates chronic tendinopathy, the presence of calcifications, or when conventional treatments have been ineffective.
The core advantage of 810nm 980nm laser therapy lies in its non-invasive and comfortable approach to reducing inflammation, relieving pain, and promoting repair at the cellular level. Laser therapy is a more ideal choice when the condition is in the acute inflammatory phase, in the early stages of soft tissue injury, or when the patient is sensitive to pain and requires gentle treatment.
https://www.arfurlamed.com/afl-medical-12-in-1/facial-endo-laser-bodylift-lipolysis-laser-treatment/
https://www.instagram.com/lily_arfurla/
https://www.facebook.com/lily.lu.71065
Whatsapp:+86 13937630317
email: lily@arfurla.com


1 Comment
porntude
A really good blog and me back again.