Product Details

ENT, also known as otorhinolaryngology, is a branch of medicine that deals with diagnosing and treating conditions affecting the ears, nose, and throat. ENT specialists use a variety of treatments to help their patients, including laser surgery.
ENT(Ear Nose Throat) handpiece:
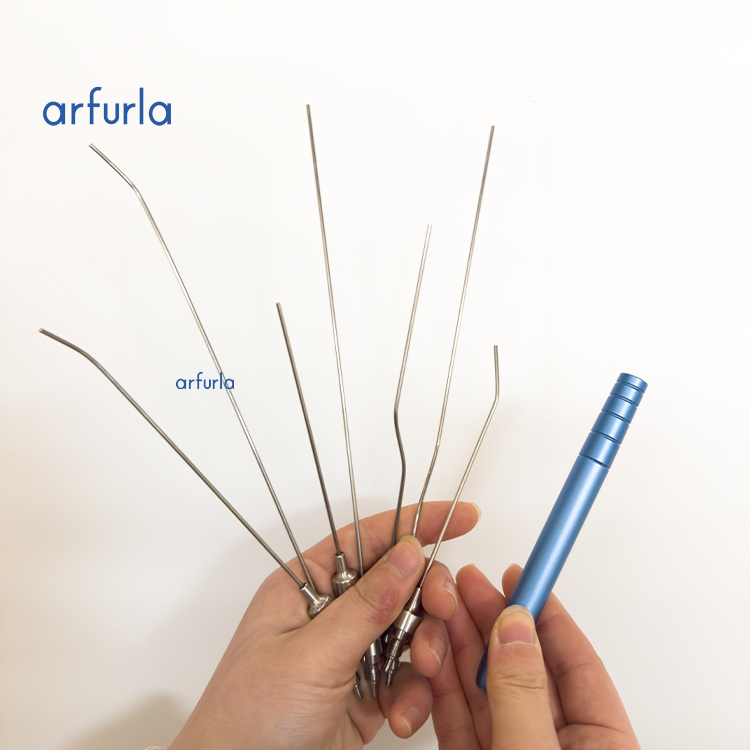
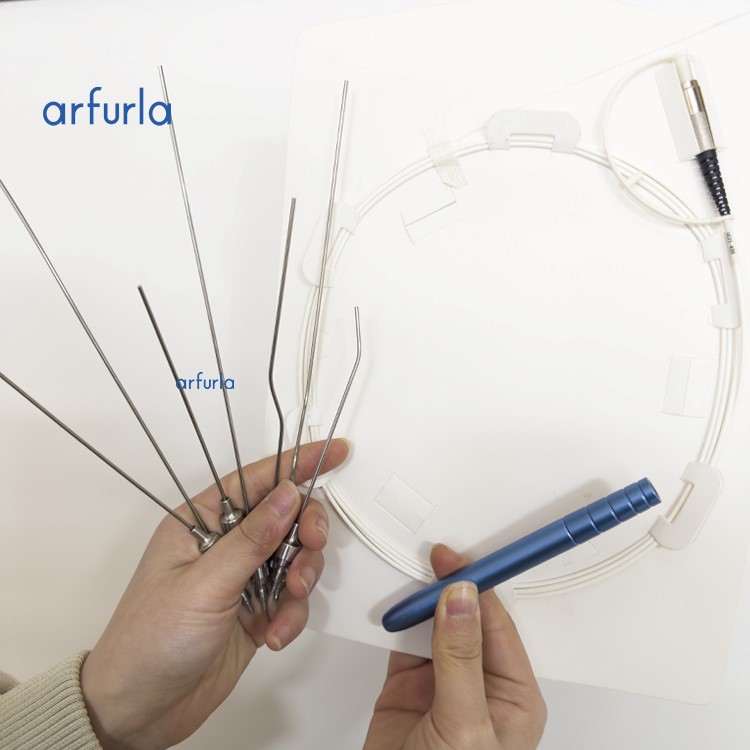
About ENT handpieces, they are mainly to do otolaryngology surgery commonly, do a few things that cut hyperplasia respect. It must install the optical fiber to use, and match with the 980nm 1470nm diode laser machine to work. The handle has in total 7 different shapes of needles that is suitable for all treatment on Ear Nose and Throat.
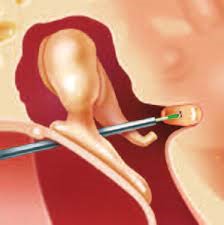
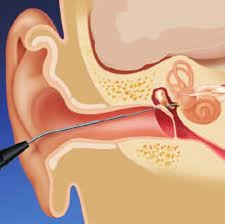
Surgical laser handpieces (applicators) are medical instruments incorporating mechanical structures to guide and secure optical fibers. This enables precise, controlled application of the laser beam to biological tissue in contact mode. Key components include a handle for freehand use, shaped fiber guide tubes, and a fixation unit. Notably, the optical fiber is a temporary connection to the handpiece.
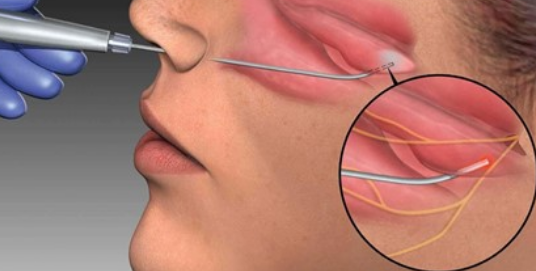
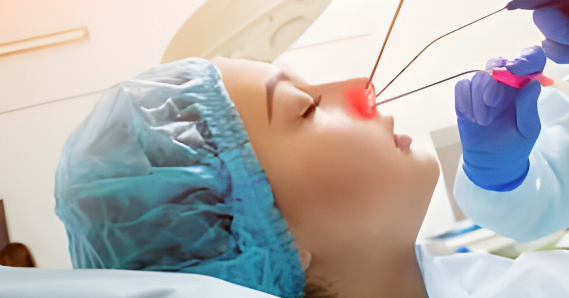
Lasers produce a focused beam of light that can cut, vaporize, or coagulate tissue. The light energy is absorbed by the targeted tissue, allowing for precise and controlled surgical interventions. This precision reduces damage to surrounding tissues, minimizes bleeding, and promotes faster healing.
Treatment part | Functions |
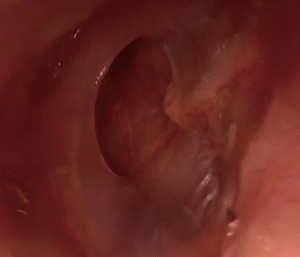 | Ear Cysts Accessory Auricle Tympanitis Hemangioma |
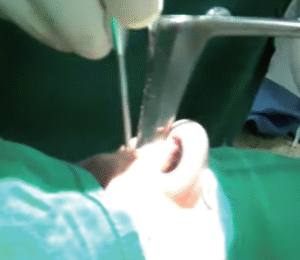 | Nose Papilloma Epistaxis Stenosis & synechia Sinus surgery |
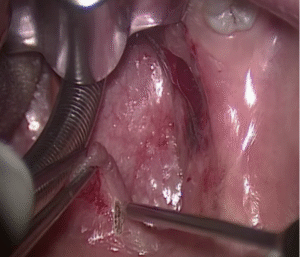 | Throat Uvulopalatoplasty Vocal cord polyps Strictures Epiglottectomy |
Applications of ENT Lasers
Rhinology:
Inferior Turbinate Volume Reduction: This is the most classic application of the 1470nm laser in rhinology. It is used to treat inferior turbinate hypertrophy caused by chronic rhinitis, vasomotor rhinitis, and other conditions. A laser fiber is inserted beneath the inferior turbinate mucosa or applied directly to its surface, vaporizing some soft tissue (submucosal ablation or surface volume reduction), reducing the turbinate and improving nasal congestion. Advantages include minimal bleeding, minimal trauma, the ability to be performed under local anesthesia, rapid postoperative recovery, and good preservation of nasal mucosal function.
Hemostasis for Nosebleeds: Direct coagulation of the bleeding site.
Loosening/Preventing Nasal Adhesions: Precisely vaporizing adhesions.
Excision of Small Nasal/Sinus Tumors: Such as polyps and papillomas.
Laryngology:
Vocal Cord Surgery: This is a strength of the 1470nm laser in laryngology.
Removal of Vocal Cord Polyps/Nodules/Cysts: Precise vaporization of the lesion provides effective hemostasis with minimal damage to the normal vocal cord mucosa, facilitating voice recovery. Laryngeal papilloma resection: Precisely vaporizes the tumor and completely stops bleeding.
Vocal groove/vocal cord scar release: Delicate operation.
Laser microsurgery for early-stage glottic laryngeal cancer (T1-T2): Using a laryngoscope and microscope, precise tumor resection is possible. The 1470nm laser ensures efficient cutting while maintaining excellent hemostasis, which is crucial for surgeries involving delicate laryngeal structures.
Laryngeal stenosis management: Releases scar tissue.
Arytenoid cartilage resection: Used for bilateral vocal cord paralysis.
Epiglottic cyst removal.
Otology:
Tympanostomy: A precise perforation is made in the tympanic membrane (e.g., to treat secretory otitis media) with minimal bleeding.
Excision of external auditory canal tumors: Such as papilloma and small cysts.
Stapes floor puncture: Used in otosclerosis surgery.

