HomePage (post) title
Category:980nm 1470nm Diode Laser Machine
Product Details
Arfurla Diode Laser Soft Tissue Cutting On Hemorrhoids Dentistry ENT
Introduction of Soft Tissue Cutting Treatment
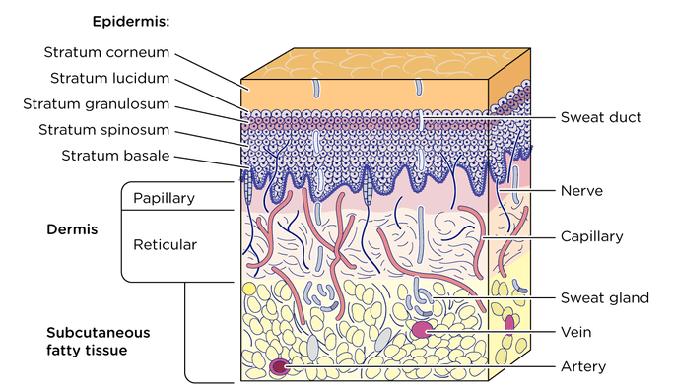
The advent of laser technology has revolutionized the field of soft tissue cutting. With unprecedented precision, it acts like an invisible “scalpel,” precisely targeting the target tissue while avoiding excessive interference with surrounding healthy tissue. Its minimally invasive nature significantly reduces pain for patients, resulting in smaller surgical incisions and significantly less discomfort during recovery. Furthermore, this technology effectively improves patient outcomes, reduces postoperative complications, and allows for a safer and more comfortable recovery.

Among the many laser wavelengths available, Arfurla 980nm and 1470nm lasers stand out as highly effective tools in soft tissue surgery. The clinical effectiveness of these two lasers stems from their unique interactions with tissue components. The 980nm laser has a strong absorption capacity for hemoglobin and is also partially absorbed by water. This property enables it to precisely cut tissue and effectively seal blood vessels when treating soft tissue involving blood vessels, thereby reducing intraoperative bleeding. The 1470nm laser, on the other hand, has an extremely high absorption rate for water and can quickly convert energy into heat, making it more efficient when vaporizing and cutting soft tissue, while minimizing thermal damage and providing better protection for surrounding tissue.

Key Applications of Soft Tissue Cutting
- General Surgery: Incisions for accessing internal organs or removing tumors.
- Dermatology: Removal of skin lesions, moles, or cosmetic procedures.
- Ophthalmology: Precision cutting in corneal or retinal surgeries.
- ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat): Procedures such as tonsillectomy or sinus surgery.
- Urology and Gynecology: Minimally invasive procedures for tissue removal or repair.
- Dentistry: Gum reshaping or oral surgeries.

Factors Influencing Soft Tissue Cutting Laser Treatment
- Tissue Type:
Different tissues (e.g., skin, muscle, fat) have varying densities and vascularity, requiring tailored cutting techniques.
- Precision and Control:
The ability to make precise incisions without damaging adjacent structures is critical, especially in sensitive areas.
- Hemostasis:
Effective control of bleeding during cutting is essential to maintain visibility and ensure patient safety.
- Thermal Damage:
Minimizing heat generation during cutting prevents unintended tissue damage.
5.Healing and Recovery:
Techniques that promote faster healing and reduce scarring are preferred.

Advantages of Arfurla 980nm and 1470nm Lasers in Soft Tissue Cutting
Precision Soft Tissue Cutting:Both lasers offer high precision, allowing surgeons to target specific tissues without damaging adjacent structures.
The 1470nm laser, in particular, excels in delicate procedures due to its shallow penetration and strong water absorption.
Minimally Invasive Soft Tissue Cutting:Laser cutting minimizes the need for large incisions, reducing trauma and promoting faster healing.
The 980nm laser’s ability to coagulate while cutting further reduces bleeding and enhances visibility during surgery.
Reduced Thermal Damage Soft Tissue Cutting:The controlled energy delivery of both lasers minimizes thermal damage to surrounding tissues.
The 1470nm laser’s shallow penetration ensures that heat is confined to the target area.
Versatility Soft Tissue Cutting:The 980nm laser’s balanced absorption by water and hemoglobin makes it suitable for a wide range of tissues, including vascularized and dense tissues.
The 1470nm laser is particularly effective in water-rich tissues, such as those found in the prostate, nasal cavity, or intervertebral discs.
Enhanced Patient Outcomes Soft Tissue Cutting:Reduced bleeding, swelling, and scarring contribute to faster recovery times and improved patient satisfaction.
Both lasers are associated with lower postoperative pain and infection rates compared to traditional cutting methods.